More than 25% percent of India’s population can neither read nor write. Rural public schools are inadequate and often non-existent. Many indirect benefits of a basic education include poverty reduction, disease control, and enhanced employment opportunities.
What is Literacy?
UNESCO defines literacy as the “ability to identify, understand, interpret, create, communicate, compute, and use printed and written material associated with varying contexts.”
Why Is Literacy Important?
In today’s society, being literate is a requirement to hold jobs that pay above minimum wage. Improving literacy and education will enhance earning potential and reduce poverty. Education can also be used to improve preventative health care.
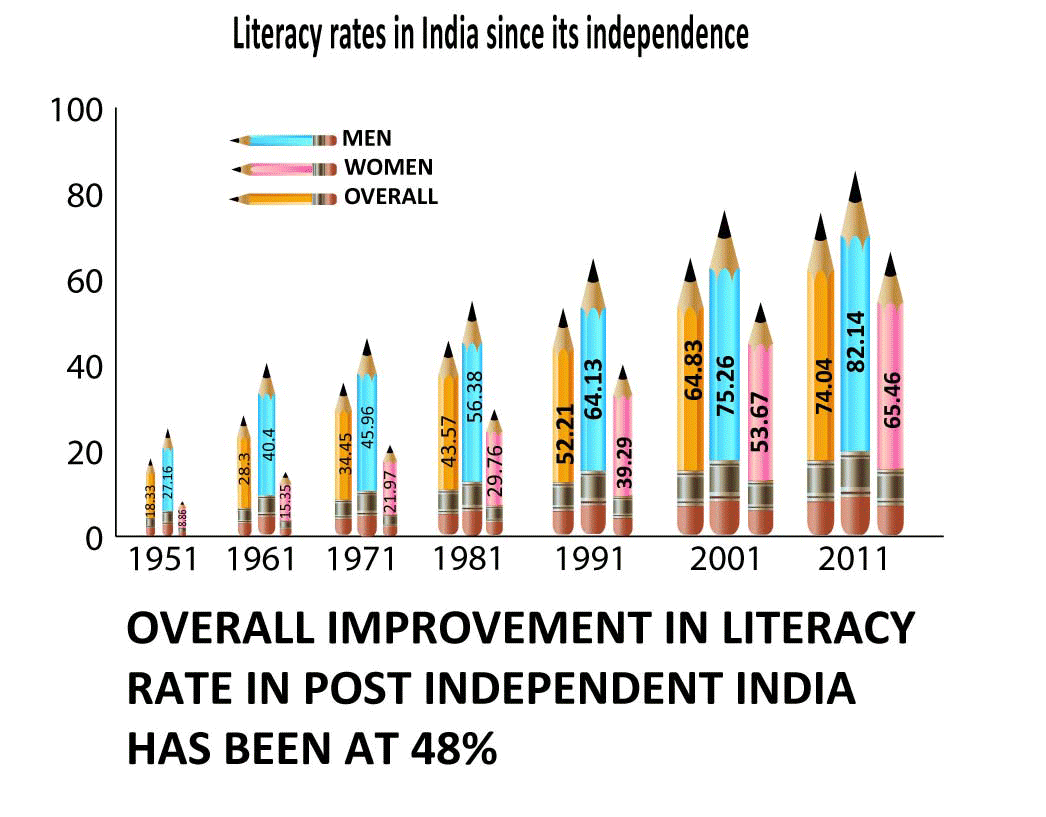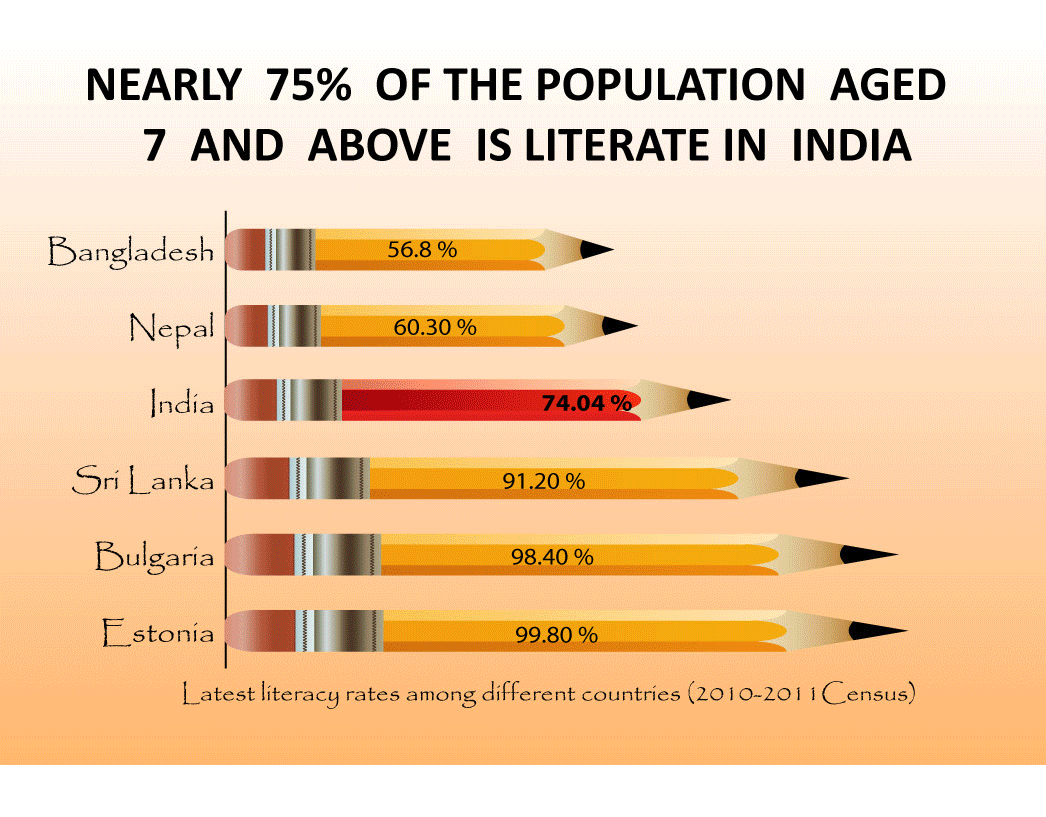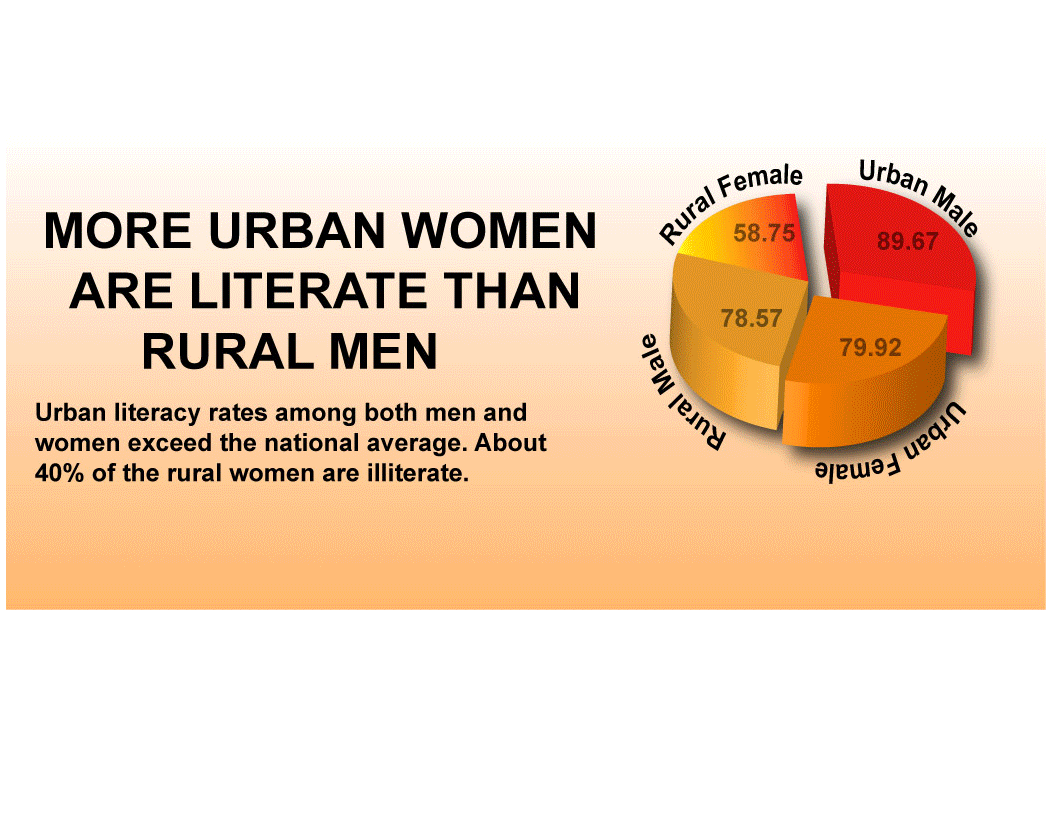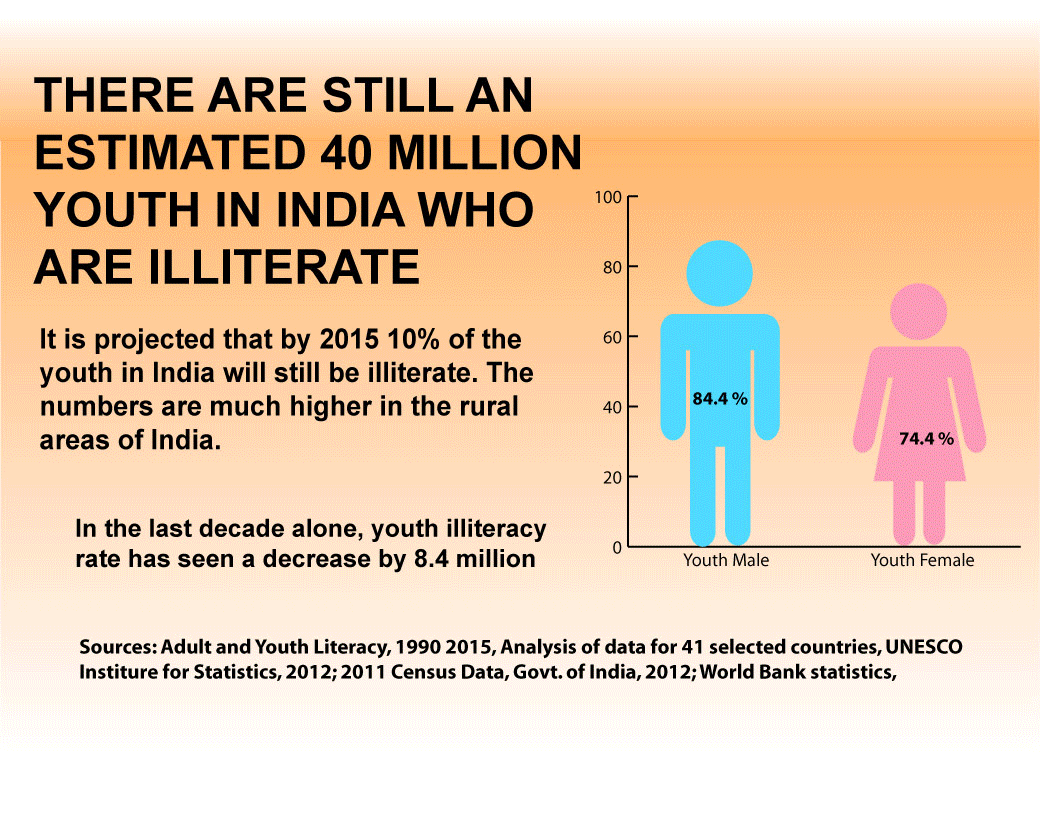
General Facts about Literacy in India:
- India has the largest illiterate population in the world.
- Almost 25% of India’s population is illiterate and cannot read or write.
- As of 2011, the literacy rate for men is 82%, and for women it is 65%.
Conditions that impact learning in rural India:
- Teacher to student ratio extremely high, leading to little individual attention
- Shortage of qualified teachers
- Teachers have high absentee rates
- Teachers have limited education
- Difficult to recruit teachers to relocate to remote villages
- Lack of well developed curriculum all textbook based, no hands-on learning
- Schools may not have:
- Drinking water
- Restrooms
- Electricity
- A library
- A Science Lab
- Computers
